Java
语法
hello world
1
2
3
4
5
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World");
}
}
|
运行时会生成.class文件,就是类,可以用javac 1.java生成类文件然后再java Main执行helloworld
注释
单行//,多行/**/
还有javadoc的文档注释
1
2
3
4
|
//javadoc文档注释
/**
* @Author gulu
*/
|
数据类型
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//System.out.println("Hello World");
long a= 10L;
float b=10f;
double c=10d;
boolean d=true;
System.out.println(a);//10
System.out.println(b);//10.0
System.out.println(c);//10.0
System.out.println(d);//true
}
}
|
变量
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class demo1 {
static double a = 1.0;//类变量static
String name;//实例变量
int age;
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i=10;//局部变量
System.out.println(i);
demo1 obj = new demo1();//实例化类
System.out.println(obj.age);
System.out.println(obj.name);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
|
常量加final
运算符
幂运算,导入Math类
1
2
|
double a=Math.pow(2,3);
System.out.println(a);
|
包
package
引入别人包用import package xxx.xxx.xxx
JavaDoc生成文档
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class Doc{
String name;
/**
*
* @param name
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
public String test(String name) throws Exception{
return name;
}
}
|
命令行
1
|
javadoc -encoding xxx -charset xxx xxx.java
|
Scanner
next和hasNext搭配,识别空格前的字符,输出不带空格
nextLine和hasNextLine搭配,识别回车前的字符,输出带空格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import java.util.Scanner;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner s=new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("用next接收: ");
if (s.hasNextLine()) {
String s1=s.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入的内容为:"+s1);
}
s.close();
}
}
|
还有nextInt、nextFloat等,识别数据类型的
循环
增强for循环
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[]a={1,2,3,4,5};
for(int x:a){
System.out.println(x);
}
}
}
|
方法
像函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum=add(1,2);
System.out.println(sum);
}
public static int add(int a,int b){
return a+b;
}
}
|
可变参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main a=new Main();
a.test(1,2,3);
}
public void test(int...a){
System.out.println(a[0]);
}
}
|
int...数据类型后面加...
数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] num;
num=new int[10];
for (int i = 0; i < num.length; i++) {
num[i]=i;
System.out.println(num[i]);
}
}
}
|
创建有两种方式
1
2
|
int[] num;
int num[];
|
对象
利用new关键字创建对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Doc{
String name;
int age;
public void study(){
System.out.println(this.name);
}
}
|
在main里面创建
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Doc xiaoming = new Doc();
Doc xh = new Doc();
xiaoming.name = "xiaoming";
xh.name = "xh";
xiaoming.age = 20;
xh.age = 10;
System.out.println(xiaoming.name);
System.out.println(xh.age);
System.out.println(xiaoming.age);
System.out.println(xh.name);
}
}
|
构造器
一个类什么都不写也会生成构造器,与类名相同
使用new关键字本质上是调用构造器,用来初始化值
有参构造:一旦定义有参构造,无参构造必须显示定义
IDEA的快捷键生成构造器AIt+insert
封装
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
|
public class Doc{
private String name;
private int age;
private String gender;
public String getName(){
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name){
this.name = name;
}
}
|
private属性就不能直接被访问了,要用public方法才能调用
main里面
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Doc xiaoming = new Doc();
// xiaoming.name = "xiaoming";
// System.out.println(xiaoming.name);
xiaoming.setName("xiaoming");
System.out.println(xiaoming.getName());
}
}
|
如果直接用.name会报错
关于生成封装也可以用前面快捷键AIt+insert
继承
extends关键字用于子类继承父类,所有类都继承父类Object类,跟ruby一样(
super关键字用于调用父类中的变量
父类
1
2
3
|
public class Doc{
protected String name="aaa";
}
|
子类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public class Main extends Doc{
public String name="bbb";
public void test(String name){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(this.name);
System.out.println(super.name);
}
}
|
实例化子类
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Main a=new Main();
a.test("666");
}
}
|
会依次输出666,bbb,aaa
如果父类的方法是private无法被继承
重写是父类与子类之间的,方法名一样,子类通过@Override注释来重写父类方法
不能是静态方法,就是没有static关键字
多态
子类型可以用父类型来创建
1
2
3
|
Student s1=new Student();
Person s2=new Student();
Object s3=new Student();
|
如果调用父类与子类相同方法,考虑子类的重写
父类调用子类子类方法要类型强转弱
子类有方法eat()
父类调用要
抽象类
abstract关键字只有方法名字没有方法实现
1
2
3
|
public abstract class aaa{
public abstract void test();
}
|
他的子类必须重写他的方法,如果他的子类也是抽象类就不要了
抽象类也不能用new,必须要用子类来实现方法
接口
interface关键字
接口中不能写方法,需要有实现类
类实现接口要用implenments关键字
接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public interface Usersevice {
void add(String name);
void remove(String name);
void update(String name);
void check(String name);
}
|
实现接口的类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
public class UserserviceImpl implements Usersevice{
@Override
public void remove(String name) {
}
@Override
public void add(String name) {
}
@Override
public void update(String name) {
}
@Override
public void check(String name) {
}
}
|
一个类可以多继承接口
内部类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public class out {
public int id =999;
public void outer(){
System.out.println("outer method");
}
public class in{
public void inner(){
System.out.println("inner method");
}
}
}
|
调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Doc{
public static void main(String[] args) {
out a = new out();
out.in b = a.new in();
b.inner();
}
}
|
可以用这种方式来获取私有属性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public class out {
private int id =999;
public class in{
public void getid(){
System.out.println(id);
}
}
}
|
调用
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public class Doc{
public static void main(String[] args) {
out a = new out();
out.in b = a.new in();
b.getid();
}
}
|
会输出私有属性id999
异常
try关键字监控区域,catch捕获异常,finally无论结果都会执行
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public class Doc{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a=1;
int b=0;
try{
System.out.println(a/b);
}catch(ArithmeticException e){
System.out.println("Arithmetic Exception");
}finally{
System.out.println("finally");
}
}
}
|
catch里面填想要捕获的类型,最高的是Throwable
throw关键字在方法中主动抛出异常
1
|
throw new ArithmeticException();
|
throws关键字在类主动抛出异常
1
|
public void test(int a,int b) throws ArithmeticException{}
|
自定义异常
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
public class myexception extends Exception{
private int details;
public myexception() {
this.details = 0;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "myexception{" +
"details=" + details +
'}';
}
}
|
多线程
继承Thread类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
package threaddemo;
//继承Thread类,重写run方法,调用start开启线程
public class thread1 extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
//run方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("aaa"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
thread1 t1 = new thread1();
t1.start();//开启线程
//main线程,主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
|
两条线程同时执行,如果直接调用run方法会先执行run,调用start方法开启多线程,会交替执行
commons.io包的使用
官网下载包之后
新建一个目录叫lib,把包放进去,右键把目录添加为库就行了
练习用多线程下载图片
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
|
package threaddemo;
import org.apache.commons.io.FileUtils;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
public class thread2 extends Thread {
private String url;
private String name;
public thread2(String url, String name) {
this.url = url;
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void run() {
webdownloader webdownloader = new webdownloader();
webdownloader.download(url, name);
System.out.println("Download complete,and filename: " + name);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
thread2 t1 = new thread2("https://haowallpaper.com/link/common/file/previewFileImg/15680526683050304", "1.png");
thread2 t2 = new thread2("https://haowallpaper.com/link/common/file/getCroppingImg/15758357910360384", "2.png");
thread2 t3 = new thread2("https://haowallpaper.com/link/common/file/getCroppingImg/16732268995923328", "3.png");
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
}
}
class webdownloader{
public void download(String url,String name){
try {
FileUtils.copyURLToFile(new URL(url),new File(name));
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("io异常");
}
}
}
|
调用runnable接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package threaddemo;
public class thread3 implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
//run方法线程体
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("aaa"+i);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
thread3 thread3 = new thread3();//创建runnable接口实现类对象
// Thread thread1 = new Thread(thread3);//创建线程对象,通过线程对象开启线程,代理
// thread1.start();
new Thread(thread3).start();
//main线程,主线程
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
System.out.println("main"+i);
}
}
}
|
感觉对后面学反序列化没有用,用到再学
反射
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package reflectiontest;
public class demo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//通过反射获取类的Class对象
Class c1 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.User");
System.out.println(c1);
Class c2 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.User");
//一个类在内存中只有一个Class对象
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
}
}
class User{
private String name;
private int age;
private int id;
public User() {
}
public User(String name, int age, int id) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.id = id;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "User{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", id=" + id +
'}';
}
}
|
获取Class类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
package reflectiontest;
public class demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person person = new Student();
System.out.println(person.name);
//方式一:通过对象获得
Class c1 = person.getClass();
System.out.println(c1.hashCode());
//方式二:forname获得
Class c2 = Class.forName("reflectiontest.Student");
System.out.println(c2.hashCode());
//方式三:通过类名.class获得
Class c3 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c3.hashCode());
//方式四:基本内置类型的包装类都有一个Type属性
Class c4 = Integer.TYPE;
System.out.println(c4);//int
//获得父类类型
Class c5 = c1.getSuperclass();
System.out.println(c5);
}
}
class Person {
public String name;
public Person() {
}
public Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
class Student extends Person {
public Student() {
this.name = "Student";
}
}
class Teacher extends Person {
public Teacher() {
this.name = "Teacher";
}
}
|
所有类型的Class对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
|
package reflectiontest;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
public class demo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Class c1 = Object.class;//类
Class c2 = Comparable.class;//接口
Class c3 = String[].class;//一维数组
Class c4 = int[][].class;//二维数组
Class c5 = Override.class;//注解
Class c6 = ElementType.class;//枚举类型
Class c7 = Integer.class;//基本数据类型
Class c8 = void.class;//void
Class c9 = Class.class;//Class
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
System.out.println(c4);
System.out.println(c5);
System.out.println(c6);
System.out.println(c7);
System.out.println(c8);
System.out.println(c9);
//只要元素类型和维度一样,就是同一个Class
int [] a =new int[10];
int [] b =new int[100];
System.out.println(a.getClass().hashCode());
System.out.println(b.getClass().hashCode());
}
}
|
类的初始化
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
package reflectiontest;
public class demo4 {
static {
System.out.println("Main");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
//主动引用
//Son son = new Son();
//反射也会主动引用
//Class.forName("reflectiontest.Son");
//不会产生类的引用的方法
//System.out.println(Son.b);
//Son[] sons = new Son[10];
System.out.println(Son.M);
}
}
class Father {
static int b=3;
static {
System.out.println("Father");
}
}
class Son extends Father {
static {
System.out.println("Son");
m=300;
}
static int m =100;
static final int M=1;
}
|
类加载器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
package reflectiontest;
public class demo5 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//获取系统类的加载器
ClassLoader classLoader = ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader();
System.out.println(classLoader);
//获取类加载器的父类加载器——>扩展类加载器
ClassLoader parent = classLoader.getParent();
System.out.println(parent);
//获取扩展类加载器的父类加载器——>根加载器
ClassLoader parent1 = parent.getParent();
System.out.println(parent1);
}
}
|
获得类名getName,getSimpleName只获得名字,获得类属性getFields,找到public属性,getDeclaredFields获得全部属性,getMethods获得本类和父类的public方法,getDeclaredMethods获取本类的所有方法,getConstructors获得构造器
利用反射动态创建对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
package reflectiontest;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class demo6 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class c1=Class.forName("reflectiontest.User");
// User user=(User)c1.newInstance();//无参构造
// System.out.println(user);
// Constructor constructor=c1.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class,int.class,int.class);//有参构造
// User c2=(User)constructor.newInstance("aaa",1,2);
// System.out.println(c2);
User c3 = (User)c1.newInstance();//通过反射调用普通方法
Method setName = c1.getDeclaredMethod("setName", String.class);
setName.invoke(c3, "test");
System.out.println(c3.getName());
User c4 = (User)c1.newInstance();
Field name=c1.getDeclaredField("name");
name.setAccessible(true);
name.set(c4,"test2");
System.out.println(c4.getName());//权限不够,元素是私有的,用setAccessible关闭安全检测
}
}
|
Springboot
用maven创建springboot项目
本地端口可以在application.properties里面更改
接下来启动main,访问8080出现error界面就成功了
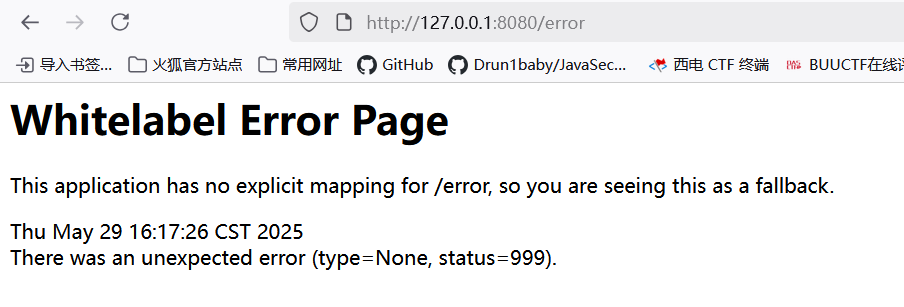
接下来输出hello,world
先在main.java的同级目录下面创接口
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package com.test.springtest.controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
public class hellocontroller {
@RequestMapping("/hello")
public String hell(){
return "hello,world";
}
}
|
可以在IDEA右侧的maven控制台打包为jar,这样就可以不启动IDEA,就能在本机8080端口运行了
pom.xml
- spring-boot-dependencies:核心依赖在父工程中
启动器
-
1
2
3
4
|
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
|
主程序
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
package com.test.springtest;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication//标注这个类是一个springboot的应用
public class SpringtestApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//启动springBoot应用
SpringApplication.run(SpringtestApplication.class, args);
}
}
|
yaml语法
前下的端口配置在yaml里是这样的
:后面一定要跟空格
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
# 普通的key-value
name: abc
# 对象
student:
name: abc
age: 111
# 行内写法
student: {name: abc,age: 111}
# 数组
pets:
- cat
- dog
- pig
pets: [cat,dog,pig]
|
yaml可以注入到配置类中
在实体类中用@ConfigurationProperties注解就能注入值,用prefix指定对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
package com.test.springtest.value;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix="person")
public class person {
private String name;
private int age;
private Boolean happy;
private Date date;
private Map<String,Object> maps;
private List<Object> lists;
public person() {
}
public person(String name, int age, Boolean happy, Date date, Map<String, Object> maps, List<Object> lists) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this.happy = happy;
this.date = date;
this.maps = maps;
this.lists = lists;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public Boolean getHappy() {
return happy;
}
public Date getDate() {
return date;
}
public Map<String, Object> getMaps() {
return maps;
}
public List<Object> getLists() {
return lists;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setHappy(Boolean happy) {
this.happy = happy;
}
public void setDate(Date date) {
this.date = date;
}
public void setMaps(Map<String, Object> maps) {
this.maps = maps;
}
public void setLists(List<Object> lists) {
this.lists = lists;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "person{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
", happy=" + happy +
", date=" + date +
", maps=" + maps +
", lists=" + lists +
'}';
}
}
|
定义完一个person类之后,用yaml来给对象赋值
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
person:
name: abc
age: 111
happy: true
date: 2022/01/11
maps:
k1: v1
k2: v2
lists:
- music
- abc
- code
|
最后在test里面执行,先引入person类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
package com.test.springtest;
import com.test.springtest.value.person;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class SpringtestApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private person person;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
System.out.println(person);
}
}
|
还能指定加载配置文件
1
|
@PropertySource(value = "classpath:application.properties")
|
赋值就麻烦了
1
2
|
//SPEL表达式取值
@Value("${name}")
|
JSR303校验
下面的class可以指定格式来校验,比如邮箱格式
springboot的多环境配置:可以选择激活哪一个配置文件
比如我们新建了application-dev.properties,在application.properties里面这样激活
1
|
spring.profiles.active=dev
|
yaml更简单
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles:
active: dev
---
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles: dev
---
server:
port: 8080
spring:
profiles: test
|
web开发
导入静态资源,去webjars官网下jquery,用maven引入
测试url
1
|
http://127.0.0.1:8080/webjars/jquery/3.7.1/jquery.js
|
读源码发现classpath有多个可以被解析
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
public void addResourceHandlers(ResourceHandlerRegistry registry) {
if (!this.resourceProperties.isAddMappings()) {
logger.debug("Default resource handling disabled");
} else {
this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getWebjarsPathPattern(), "classpath:/META-INF/resources/webjars/");
this.addResourceHandler(registry, this.mvcProperties.getStaticPathPattern(), (Consumer)((registration) -> {
registration.addResourceLocations(this.resourceProperties.getStaticLocations());
if (this.servletContext != null) {
ServletContextResource resource = new ServletContextResource(this.servletContext, "/");
registration.addResourceLocations(new Resource[]{resource});
}
}));
}
}
|
跟进resourceProperties
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
public static class Resources {
private static final String[] CLASSPATH_RESOURCE_LOCATIONS = new String[]{"classpath:/META-INF/resources/", "classpath:/resources/", "classpath:/static/", "classpath:/public/"};
private String[] staticLocations;
private boolean addMappings;
private boolean customized;
private final Chain chain;
private final Cache cache;
|
- /resources/
- /static/
- /public/
- /META-INF/resources/
注意:不要轻易去该配置文件里面
1
2
3
|
spring:
mvc:
static-path-pattern: /**
|
如果把前端代码写到templates下面,要用controller来跳转,而且要模板引擎来渲染
这里用Thymeleaf,
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
|
public class ThymeleafProperties {
private static final Charset DEFAULT_ENCODING;
public static final String DEFAULT_PREFIX = "classpath:/templates/";
public static final String DEFAULT_SUFFIX = ".html";
private boolean checkTemplate = true;
private boolean checkTemplateLocation = true;
private String prefix = "classpath:/templates/";
private String suffix = ".html";
private String mode = "HTML";
private Charset encoding;
private boolean cache;
private Integer templateResolverOrder;
private String[] viewNames;
private String[] excludedViewNames;
private boolean enableSpringElCompiler;
private boolean renderHiddenMarkersBeforeCheckboxes;
private boolean enabled;
private final Servlet servlet;
private final Reactive reactive;
|
可以看到在templates目录下以html为后缀的才被解析
controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
package com.test.springtest.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class index {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(){
return "test";
}
}
|
只要在templates下写同名的html,就能被渲染
thymeleaf语法
跟着中文文档来教程:使用 Thymeleaf - 中文文档
controller
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
package com.test.springtest.controller;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
@Controller
public class index {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "哈基米南北绿豆");
return "test";
}
}
|
test.html
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en" xmlns:th="http://www.thymeleaf.org">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<!--所有的html元素都能被thymeleaf替换 th:元素名-->
<div th:text="${msg}"></div>
</body>
</html>
|
总结
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
简单表达式:
变量表达式:${...}
选择变量表达式:*{...}
消息表达式:#{...}
链接URL表达式:@{...}
片段表达式:~{...}
|
数据库这里直接跳了
springsecurity
Spring Security 中文文档 :: Spring Security Reference
shiro
Apache Shiro | Java Security Framework
shiroconfig.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
package com.test.springtest.config;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.spring.web.ShiroFilterFactoryBean;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
import org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.DefaultWebSecurityManager;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import java.util.LinkedHashMap;
import java.util.Map;
@Configuration
public class shiroconfig {
@Bean
public ShiroFilterFactoryBean getShiroFilterFactoryBean(@Qualifier("securityManager") DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager) {
ShiroFilterFactoryBean bean = new ShiroFilterFactoryBean();
bean.setSecurityManager(securityManager);
/*
* anno:无需认证
* authc:必须认证
* user:必须remeberme
* perms:拥有某个资源权限
* role:拥有某个角色权限
* */
Map<String, String> filterChainDefinitionMap = new LinkedHashMap<>();
filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/user/add", "anno");
filterChainDefinitionMap.put("/user/update", "anno");
bean.setFilterChainDefinitionMap(filterChainDefinitionMap);
bean.setLoginUrl("/login");
return bean;
}
@Bean
public DefaultWebSecurityManager securityManager(@Qualifier("userRealm") userrealm userRealm) {
DefaultWebSecurityManager manager = new DefaultWebSecurityManager();
manager.setRealm(userRealm);
return manager;
}
@Bean
public userrealm userRealm(){
return new userrealm() {
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
return super.doGetAuthorizationInfo(principalCollection);
}
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
return super.doGetAuthenticationInfo(authenticationToken);
}
};
}
}
|
userrealm.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
package com.test.springtest.config;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.AuthenticationToken;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.credential.CredentialsMatcher;
import org.apache.shiro.authz.AuthorizationInfo;
import org.apache.shiro.cache.CacheManager;
import org.apache.shiro.realm.AuthorizingRealm;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.PrincipalCollection;
public abstract class userrealm extends AuthorizingRealm {
//授权
@Override
protected AuthorizationInfo doGetAuthorizationInfo(PrincipalCollection principalCollection) {
System.out.println("授权doGetAuthorizationInfo");
return null;
}
//认证
@Override
protected AuthenticationInfo doGetAuthenticationInfo(AuthenticationToken authenticationToken) throws AuthenticationException {
System.out.println("认证doGetAuthenticationInfo");
return null;
}
}
|
index.java
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
package com.test.springtest.controller;
import org.apache.shiro.SecurityUtils;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.IncorrectCredentialsException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UnknownAccountException;
import org.apache.shiro.authc.UsernamePasswordToken;
import org.apache.shiro.subject.Subject;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Controller
public class index {
@RequestMapping({"/index","/"})
public String test(Model model) {
model.addAttribute("msg", "哈基米南北绿豆");
model.addAttribute("users", Arrays.asList("哈基米","曼波"));
return "index";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/add")
public String add(){
return "user/add";
}
@RequestMapping("/user/update")
public String update(){
return "user/update";
}
@RequestMapping("/toLogin")
public String toLogin(){
return "login";
}
@RequestMapping("/login")
public String login(String username, String password, Model model){
//获取当前用户
Subject subject = SecurityUtils.getSubject();
//封装用户登入数据
UsernamePasswordToken Token = new UsernamePasswordToken(username, password, true);
try{
subject.login(Token);
return "redirect:/index";
}catch (UnknownAccountException e){
model.addAttribute("msg", "用户名错误");
return "login";
}catch (IncorrectCredentialsException e){
model.addAttribute("msg", "密码错误");
return "login";
}
}
}
|

